This post will show how to create a Student Enrollment Application using MYSQL DB with Hibernate ORM in a Spring environment. This is a simple application that aims to collect the input details from the user during signup, save the details in the MYSQL DB and authenticate the same during login.
1. Create Java Web Application Project using Maven Template
To begin with, in the IDE, create a Java Maven project with the template of maven-archetype-webapp (Filter the catalog based on the string “webapp”) by providing appropriate values for GroupId and Artifact Id for the project. The sample web application directory structure is shown below with a standard deployment descriptor web.xml and Maven pom.xml
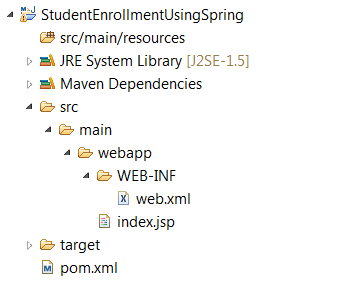
2. Update pom.xml
To make the above Maven Java Web Application project support the Hibernate ORM in Spring framework, add the following dependencies to the existing pom.xml
- jstl, spring-webmvc and servlet-api (for Spring support)
- mysql-connector-java (for MYSQL support)
- spring-jdbc (for data access with JDBC Spring)
- spring-orm (for ORM data access with Spring)
- spring-data-jpa (for JPA support)
- hibernate-validator and hibernate-entitymanager (for Hibernate Support)
- jta (for transaction support)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 | |
3. Modify web.xml
Modify the contents of the web.xml to include the following:
- A servlet and specify the location of the configuration file for the same. In this sample, a configuration file named springConfig.xml is created under WEB-INF/config folder in the project layout.
- A servlet-mapping to map the servlet created in the above step that should be invoked when the client specifies the url matching the url pattern.
- A ContextLoaderListener to integrate spring with the web application and provide the contextConfigLocation where the context files for JPA.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | |
4. Create the Spring Configuration File
Create a Spring Bean Configuration file under the folder WEB-INF/config. If a STS(Spring Tool Suite) is the IDE, go ahead and enable the context and mvc namespaces. The servletConfig.xml will be as shown below
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | |
After enabling the required namespaces, include the following (in between the <beans> and </beans> tags) to indicate that the application is annotation driven and base package for the context component scan.
1 2 3 | |
Include the bean InternalResourceViewResolver of Spring to locate the jsp files
1 2 3 4 | |
Include the bean for specifying a properties file (more on this later) which is to be used to store custom messages or properties. The following configuration allows to create a properties file named messages.properties under the src/main/resources folder in the project.
1 2 3 | |
5. Create persistence.xml
Create a file named persistence.xml under the folder src/main/resources/META-INF folder in the project to define the persistence unit required by JPA. Add the following to the persistence.xml to define a persistence unit named punit.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | |
6. Create jpaContext.xml
As defined in the web.xml, create a file named jpaContext.xml under the folder src/main/resources folder in the project to define JPA and Hibernate related configurations. Note that any file created under src/main/resources folder in a maven project will be automagically added by Maven to the classpath. If STS(Spring Tool Suite) is the IDE, go ahead and enable the context, jpa and tx namespaces. The jpaContext.xml will be as shown below
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | |
After enabling the required namespaces, include the following (in between the <beans> and </beans> tags) to indicate that the application is annotation driven and base package for the jpa repositories scan.
1 2 3 | |
Next, include the bean PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor. This is necessary to process the Persistence Unit, Persistence Context annotations and for injecting JPA related resources.
1
| |
Include the bean for EntityManagerFactory which lists the various JPA related properties/resources.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | |
Include the bean for data source, where the properties of the MYSQL DB like url, username and password can be specified. Replace <include connection url> with the actual connection url for connecting to the MYSQL DB. Likewise, replace <include username> and <include password> with the actual username and password values.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
Include the bean for transaction manager for scoping/controlling the transactions.
1 2 3 4 5 | |
Thus ends the long configuration in jpaContext.xml
7. Create JSP Files for Student Signup/Login
Create a folder named “jsp” under WEB-INF (This is where the jsp files will be created as indicated in the servletConfig.xml for the InternalResourceViewResolver bean).
Create a file signup.jsp to include a form to get the input details like UserName, Password, FirstName, LastName, DateOfBirth and EmailAddress of the student. A snapshot of the signup page is as follows:

Next, create a file login.jsp to include a form with UserName and Password. A snapshot of the login page is as follows:

Also create success.jsp to indicate the login success and failure.jsp to indicate login failure (These are just pages used to display the contents - no processing logic involved).
This application uses twitter bootstrap http://getbootstrap.com/ and http://bootswatch.com/united/ as style sheets. It also uses a datepicker stylesheet as well to pop up a calendar for the DateOfBirth field in the Student Signup page (http://www.eyecon.ro/bootstrap-datepicker/).
A reference link to the files under webapp folder of this application can be found at https://github.com/elizabetht/StudentEnrollmentWithSpring/tree/master/src/main/webapp
8. Create packages for Controller, Model, Repository and Service tier classes
Create packages each for the Spring Controller, Model, Repository and Service classes under the src/main/java folder.
A sample snapshot of the project after the package creation is as shown below:

9. Create classes for Model Tier
Create a POJO class named Student.java inside the package com.github.elizabetht.model to include the details of the Student model entity during signup. Create another POJO class named StudentLogin.java inside the same package com.github.elizabetht.model to include the Student Login details.
A reference link to the files for the Model classes can be found at https://github.com/elizabetht/StudentEnrollmentWithSpring/tree/master/src/main/java/com/github/elizabetht/model
10. Create class for Repository Tier
Create an interface class named StudentRepository.java inside the package com.github.elizabetht.repository to support the repository tier database operations.
There are two interface methods needed for the application’s purpose.
- To Insert the Student Signup details into the Database
- To Verify the Student Login details from the Database
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
The save() method is supported by the Hibernate implementation and hence no separate SQL statements are required for the data insert.
11. Create classes for Service Tier
Create an interface class named StudentService.java inside the package com.github.elizabetht.service to support the service tier operations.
1 2 3 4 5 | |
Create a service tier implementation class (a POJO indeed) named StudentServiceImpl.java inside the package com.github.elizabetht.service. This is where the application logic goes - either to save the student details into the database or to verify the student (already saved) details from the database.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | |
12. Create class for Controller Tier
Create a Controller tier POJO class named StudentController.java inside the package com.github.elizabetht.controller. This is where the routing logic of the application goes - whether a signup or login action is called.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 | |
13. Create messages.properties file
As seen above, the @Valid annotation is used to validate the input parameters of the form reaching the method and the result of the validation is stored in BindingResult object. In order to validate specific fields, (refer the classes created for the Model tier - https://github.com/elizabetht/StudentEnrollmentWithSpring/tree/master/src/main/java/com/github/elizabetht/model), use annotations like @NotEmpty, @Size, @Email and @NotNull from the various validations available from the Hibernate Validator.
The Custom messages that should be displayed when any of the above mentioned validators fail is specified in the messages.properties file. Create a file named messages.properties under src/main/resources folder and include the following
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |
14. Create the DB Schema in a MYSQL DB
Connect to the MySQL DB which is to be used for this application and create a new DB Schema named studentEnrollment using the MySQL Workbench. This is necessary as the DB Schema name of studentEnrollment is specified in the dataSource bean in jpaContext.xml
Once the studentEnrollment DB Schema is created, create a table named student inside the DB Schema using the CREATE TABLE statement as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | |
15. Deploying the Application on Tomcat Server
Once the above steps are complete and the project is successfully built, the Java web application is ready to deployed on the Tomcat Server 7.
The Java web application can be deployed locally by right clicking on the project and choosing the “Run As->Run on Server” option.
The same can be deployed remotely on any native server that supports Tomcat by copying the WAR file (Right click on the project and choose Export as WAR File option) to /var/lib/tomcat7 folder (or appropriate tomcat directory) and restarting the tomcat server.
16. Clone or Download code
If using git, clone a copy of this project here: https://github.com/elizabetht/StudentEnrollmentWithSpring.git
In case of not using git, download the project as ZIP or tar.gz file here: https://github.com/elizabetht/StudentEnrollmentWithSpring/releases/tag/1.6